Global
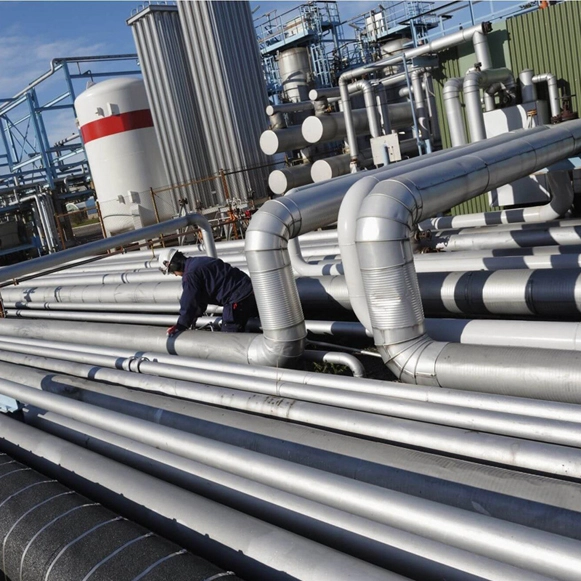
North Refractories is an innovative manufacturer of thermal insulation materials for thermal process plants and industrial insulation systems. We use the advanced materials to help customers to be safe and more energy efficient, extending lifecycle performance.
In the past 20 years, we have developed powerful and efficient products ranges to meet our customers' high quality demands for different industries, typical products include high density calcium silicate insulation materials, flexbile fiber insulation mats, ragid insulation boards, super low thermal conductivity panels, super high temperature polycrystalline fiber materials, high strength carbon fiber textiles, customized special shapes.






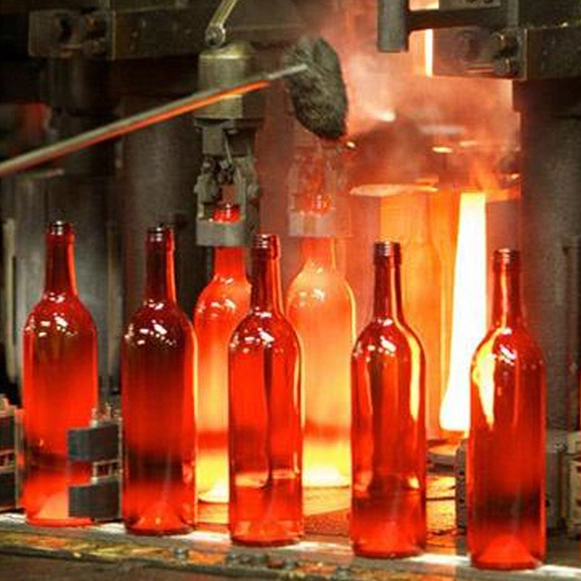
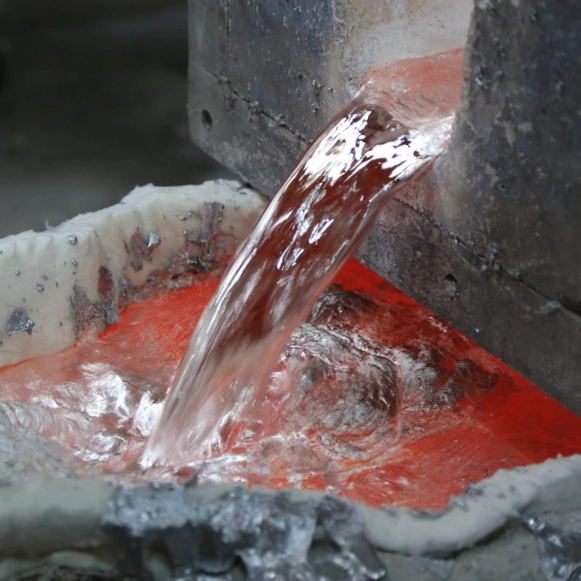
NR-80 high density calcium silicate boards have excellent properties of non-wettability and durability, super great thermal insulation performance. Because of these characters, it can be used during the manufacturing process of aluminum products and can be contacted directly with molten aluminum, such as it is used for melting of the aluminum ingot, transferring the liquid aluminum metals, holding furnaces insulation linings.
For the aluminum rolling manufacturing, aluminum casting and die-casting manufacturing, NR-80 boards are used by machining into special parts such as launders or ladles or troughs for equipment including melting furnaces, reverberating furnaces or skull crucible furnaces.
These boards or machined components improve the product quality and yield, efficiency of casting work, saving energy by reducing fuel consumption by excellent insulation performance.
NR-80 calcium silicate board is lightweight, high mechanical strength, excellent in thermal insulation and it is machinable, most important comparing with the refractory castable, NR-80 boards are more easy and convenient to install onto the equipment which will save repairing time and improve the production yield significantly , at the same time because of its excellent insulation performance it help aluminum casting factory save the energy and cost. For the installation, the boards can be processed with general woodworking tools easily and then it can fixed by bonding and screwing quickly. Based on the equipment requirements, it can be used directly in the holding furnace bath as a inner linings or processed into shapes of floats, spouts , T-plates, hot top ring headers which have very precise dimensions.






